Top 10 Tips to Build a Google-Friendly Site

These days, marketers are doing everything they can to leverage non-paid marketing channels to increase operating income and decrease spend. One of the most impactful areas of non-paid marketing is search engine optimization (SEO).
However, many businesses tackling SEO are only focusing on content marketing and social media while ignoring technical considerations important to Google and Bing. Yes, there's an echo chamber out there proclaiming that content marketing and social are the new SEO, but that couldn't be any farther from the truth.
You can publish the most effective content for your audience, share it on all of your social networks and still not yield results in the major search engines. The foundation of SEO is technical in nature and it's important to build a site that is both accessible to search engines and semantic in nature.
Here are 10 things you can do to build a Google-friendly Site:
1. URL Structure Optimization:
Often times, out of the box CMS platforms deliver URLs chock full of unnecessary parameters and irrelevant characters. URL structure is incredibly important to the crawlability and relevance of your website.
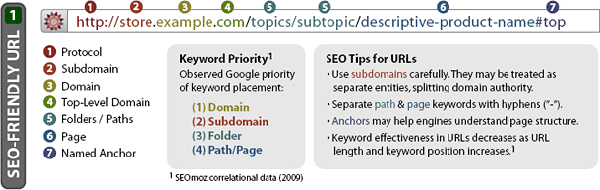
(Image Source: Moz.com)
Solution: Ensure your URLs are optimized for organic search.
2. Page Speed Optimization:
An important part of Google's ranking algorithm is the speed at which your Web pages load.
Solution: Test your page speed using Google's free tool and follow their recommendations: https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/.
3. Internal Link Optimization:
PageRank is what powers a Web page's Google rankings. The more PageRank a Web page has, the better opportunity it has to return in Google's search results. Web pages pass PageRank to the other internal pages they link to (PageRank filtration). The amount of PageRank that passes from a page to pages it links to shrinks with each additional link.
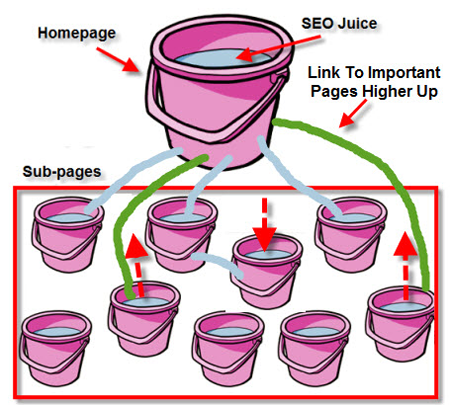
(Image Source: eVisibility)
Example: PageRank (PR) / Number Links = Amount of PageRank passed to linked pages
A PR of 8 / 40 internal links = .2 PR passed to linked pages
A PR of 8 / 10 internal links = .8 PR passed to linked pages
Solution: Audit your internal link architecture and make sure that you're not linking to non-essential pages and maximize your PageRank filtration.
4. JavaScript Optimization:
Search engine spiders have a difficult time crawling and navigating JavaScript code. Though engines are getting better at executing JS, they're not great at it. In fact, JavaScript often blocks search engines from crawling important content and links. If your website is heavy in JavaScript functionality, ensure you're coding it in an unobstructed way. Otherwise, provide search engines with other avenues of accessing content.
As an example: At my company, we fixed a JavaScript / GoogleBot issue and saw traffic, orders and revenue increase more than 100 percent from the organic channel.
5. Get Rid of Spider Traps:
It's commonplace for sites to enable pop-ups for assets like images, printable page versions, etc... and not provide a link back to the website. This causes a problem with search engines, because it traps them in the pop-up without the ability to navigate to any other content. Additionally, search engines will return pop-up pages in search results which provide a bad customer experience upon click-through.
Solution: Either block pop-up windows in your robots.txt file or include a no-follow tag in the pop-up's HTML.
6. Schema Mark-Up Optimization:
In 2011: Google, Yahoo and Bing collaborated to create new HTML code that would better help them understand the Web. This mark-up is called Schema.org. There is a variety of different schemas you can implement to help search engines recognize your products, services and content. As search engines continue to move to a more semantic approach to the Web, it's vital that you get Schema.org mark-up on your Web pages.
Solution: Audit your site's HTML and ensure you've got Schema.org mark-up where appropriate. There's also a handy little tool that can help you automate your Schema.org coding. Additionally, use Google's Schema validator to check that you've implemented correctly.
7. User-Experience Optimization:
The more usable your website is to humans, the more appealing it will be to search engines. Google has also included user experience as a signal in its Panda algorithm filter. It's important to make sure you're treating your website visitors and search engine spiders with respect and provide a quality experience.
Solution: Get an objective opinion of your website's user experience.
- You can hire lay-people to perform certain use-case scenarios, gather feedback and implement.
- You can use your site analytics to determine if there may be user-experience issues causing performance problems.
- Use your on-site search appliance data to get a sense of what people are looking for. Then make sure the keywords with the most internal searches have content easily findable in the information architecture of your Site.
8. Content/Code Prominence Optimization:
On ecommerce sites, you'll often find that an assortment of products is listed in categorical and sub-categorical pages. And below the products live a block or blocks of marketing content. While this is good for humans, it's not so much for search engines. Content that lives at the bottom of a page is seen as less important by search engines, so it's important that content be as close to the top of the page is possible.
Solution: Within the HTML, you can move the code where the content lives higher up in the DOM while keeping its placement the same in the browser rendered version.
9. Include Appropriate HTML Elements in Web Page Templates:
Search engines use HTML elements to understand the context and relevance of Web page content. Including the appropriate HTML elements on your Web page templates will give your content optimization a major boost in relevance.
Solution: Make sure your templates include: H1-H4 tags where appropriate, Meta-Descriptions, and Image ALT attributes. For more help, read this article from Moz.
10. Google Webmaster Tools:
Last but not least. Make sure you create a Google Webmaster Tools account for your Website. This will allow Google to communicate directly to you about any issues it finds on your site. Learn more at https://www.google.com/webmasters.